Applications
Example of Electronic Paper Tag Application in a Manufacturing Factory
Promoting paperless and DX-ization in factories:
Paperless operation without changing the existing manufacturing layout
Electronic paper tags are battery-less RFID tags with a display function that can be used to replace paper labels in manufacturing plants. Electronic Paper tags are used in factories for such items as physical inventory slips, process control charts, returnable containers, and production line undons.
Table of Contents
About Electronic Paper Tags
The electronic paper tag is an RFID tag with a display function that uses UHF band RFID technology and operates without batteries. Since the electronic paper tag can repeatedly update its display content, there is no need to replace the label. Since the tag is battery-less and is powered wirelessly by a reader/writer (R/W), there is no need to replace the batteries. Paper labels are often used in manufacturing plants where information needs to be visualized. Electronic paper tags not only display information as legibly as paper labels, but can also function as RFID, making it possible to go paperless. Barcodes and QR codes used in existing systems can also be displayed on electronic paper, making the introduction of electronic paper tags a smooth process.
Applications of Electronic Paper tags in manufacturing plants
1. Use of Electronic Paper tags on the actual product form
Paper labels are used for the physical product tags that contain product identification information, date and time of manufacture, processes, inspection results, and so on. However, paper labels are easily soiled or damaged on the production line, and as a result, their readability can deteriorate. In addition, printing and disposal of paper labels require a lot of man-hours and impose a burden on the environment. Replacing paper labels with electronic paper labels, therefore, reduces the man-hours required to print and replace paper labels, thereby realizing a paperless environment and reducing environmental impact at the same time.
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
|
・Increased man-hours due to printing and disposal of paper labels ・Increased environmental impact due to paper label disposal ・Decreased readability due to soiling and damage in the production line |
・Paperless system (carbon neutral and sustainable) ・No need to reapply labels by simply rewriting the face of the ticket on the R/W. ・Automatic rewriting of ticket face by linking with production information ・Reduced environmental impact due to reusability ・Wiping off soiled tickets maintains legibility. |

Electronic paper tag image of the actual goods receipt
2. Use of Electronic Paper Tags in Process Control Charts
At manufacturing sites, process control charts are operated with paper labels. Each completed work process is entered by hand, but this process can increase man-hours and cause entry errors. Since the tags can be used as RFID tags, detailed information in the process can be stored in the memory of the tag, and detailed information in the process can be checked offline using R/W.
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
|
・Increased man-hours due to manual entry ・Omissions and entry errors ・Increased costs and environmental impact due to paper disposal |
・Paperless system (carbon neutral and sustainable) ・Reduction of man-hours by automating work checks ・Elimination of entry errors and immediate grasp of production management status by linking with the system ・Detailed process information is stored in the tag's memory, Detailed information on the process can be stored in the tag's memory, making it possible to obtain process history information even when offline. |
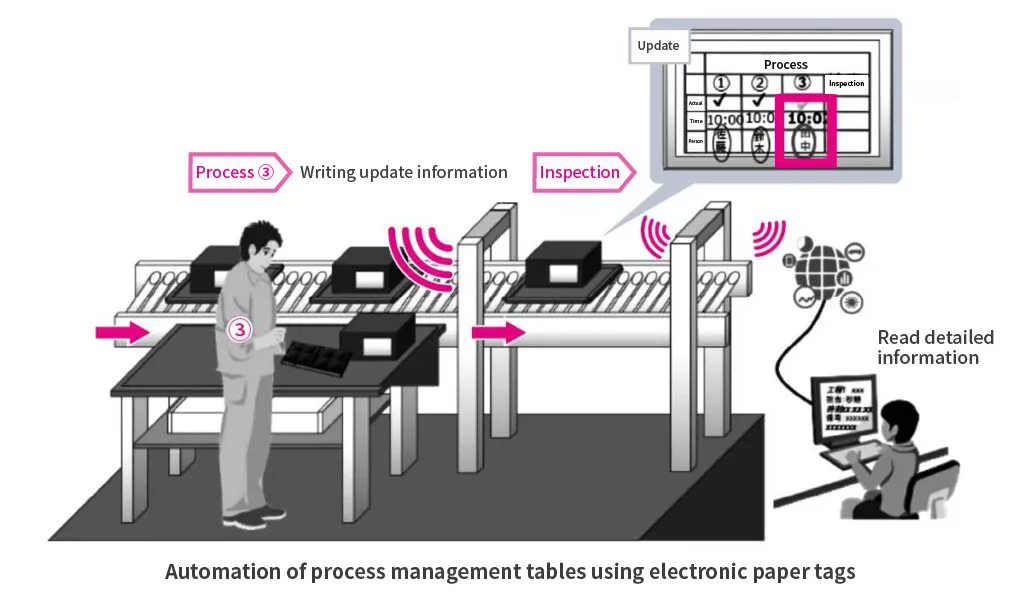

Electronic paper tag image of process control chart
3. Use of Electronic Paper tags in returnable containers
Reusable containers are used repeatedly to transport materials, parts, and products between locations. Paper labels are generally used on these boxes to clearly indicate destinations and information on materials and parts, but by introducing electronic paper tags, a paperless system can be realized, reducing the amount of time spent printing, attaching, and peeling paper labels.
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
|
・Man-hours required to replace labels (printing, attaching, and peeling) ・Increased costs and environmental impact due to paper waste ・Soiling caused by label re-covering, requiring cleaning. |
・Paperless (carbon neutral and sustainable) ・No need to reapply labels by simply rewriting the face of the ticket on the R/W. Reduced environmental impact due to reusability ・No staining due to no re-covering. ・System linkage prevents misdirection |


Electronic paper image of shelf management in a logistics warehouse
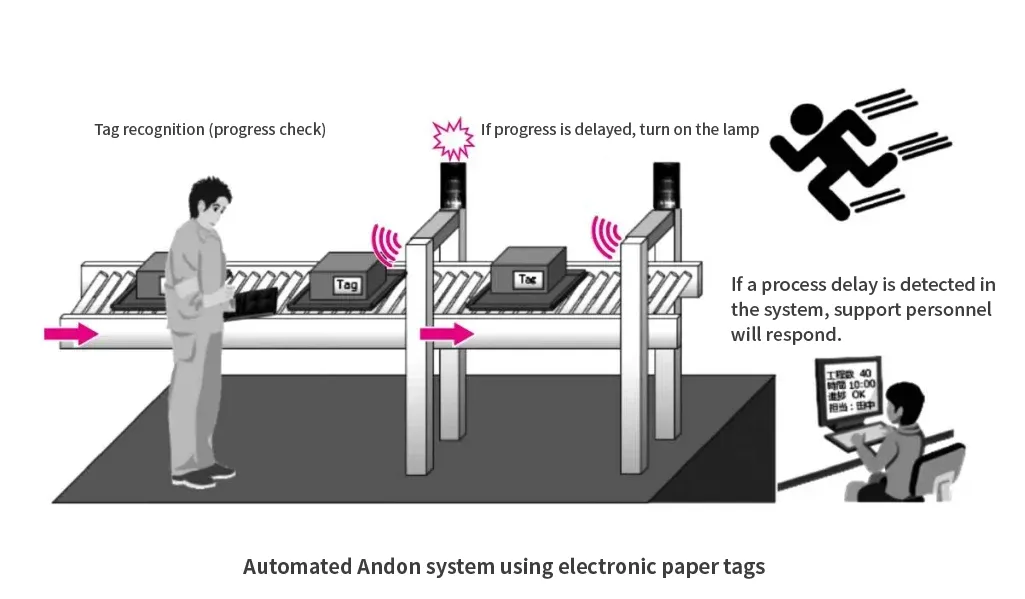
4. Automatic andon
When an abnormality occurs on a production line, an andon (indicator) is used to immediately notify those involved. In a conveyor belt line, the work time for each process is predetermined, and if work is delayed, the line may become stagnant. Therefore, if work progress is delayed, the worker presses a switch to indicate the abnormality on the andon. Because the timing of the abnormality notification differs depending on the judgment of individual workers, delays to line work may occur. By introducing electronic paper tags, progress delays can be detected automatically, leading to improved productivity.
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| When work is delayed, workers make this known by pressing a switch. However, due to differences in the judgment of individual workers, the timing of notification differs, which can cause delays in line work. |
R/W is installed on the conveyor belt line, and when an electronic paper tag moving with the product reaches the reading range and has not completed the predetermined work, the undone light is automatically turned on to notify the system of the work delay. By capturing delays automatically, anomalies are more apparent and lead to improved productivity, regardless of the operator. |